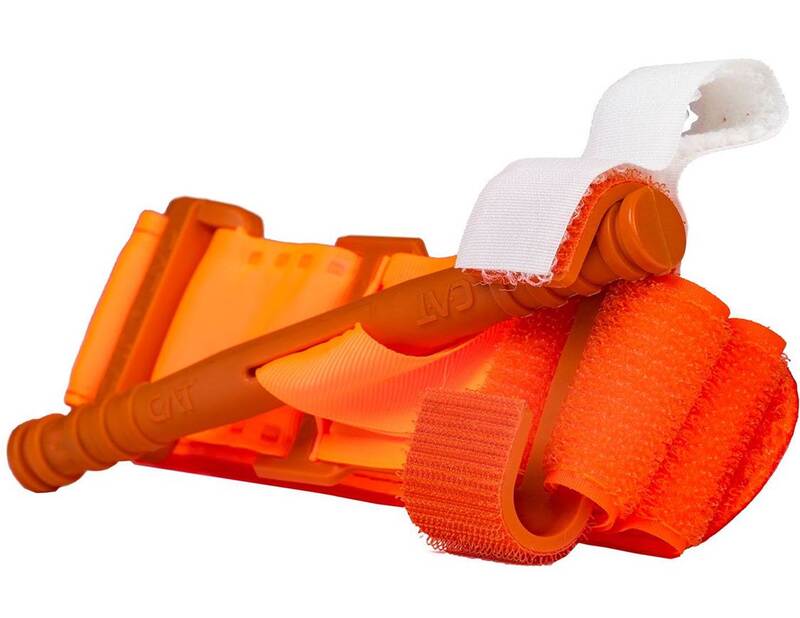
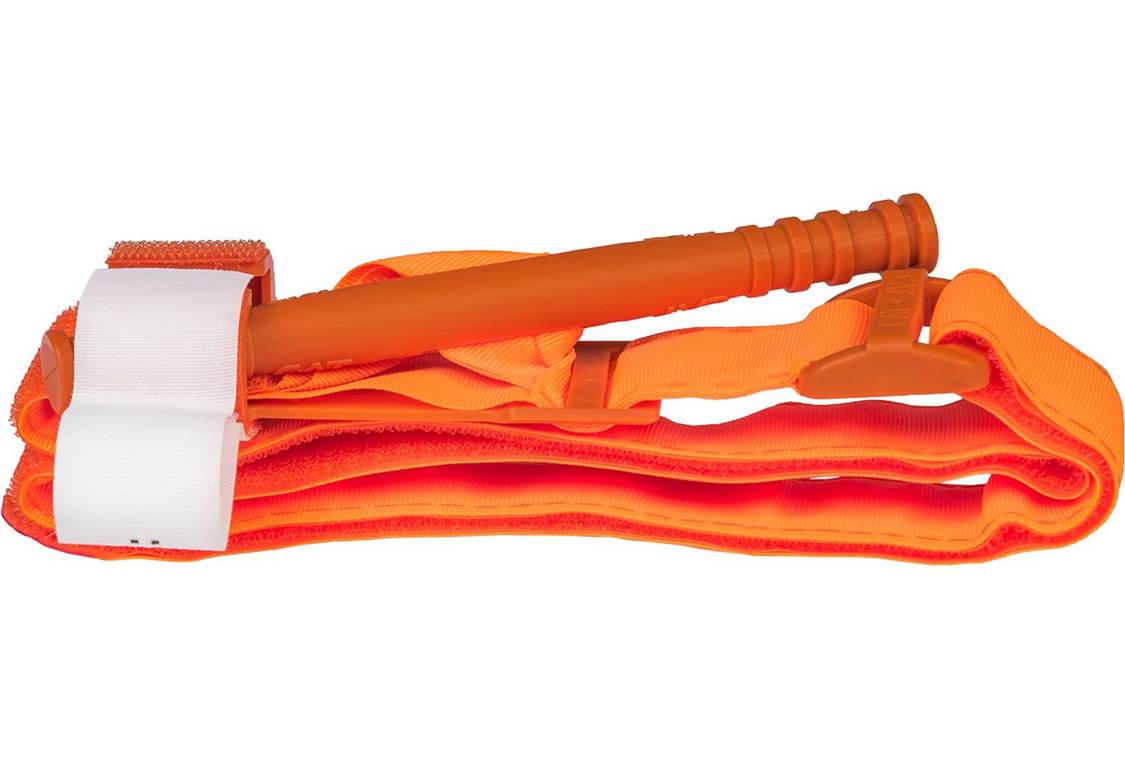
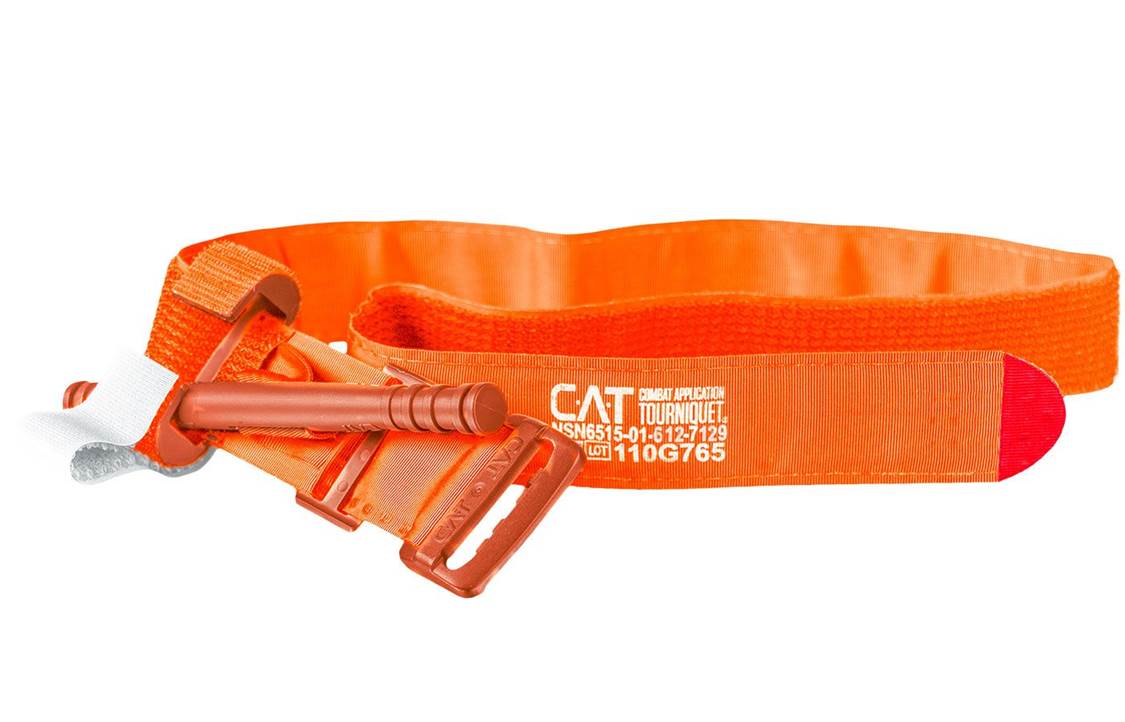
North American Rescue Combat Application Tourniquet (C-A-T) Last week I got into a discussion with a friend of mine who’s an EMT about the type of gear that you should have for emergencies where a victim is severely bleeding, and we spent a fair amount of time discussing the importance of tourniquets. Because the data (especially the data from the US military in Iraq and Afghanistan where IEDs were prevalent and body armor decreased the number of immediate deaths) shows that using tourniquets can have a significant impact on saving the lives of wounded people, I thought that I would lay out the facts in this blog. For years the approach to treating people in trauma situations was ABC (Airway, Breathing, and Circulation), but over the past 20 years the priority order for lifesaving treatments in emergency situations has transitioned to MARCH (Massive Hemorrhage, Airway, Respiration, Circulation, Hypothermia/Head Injury). So these days, upon arrival as you evaluate the person for trauma, the most notable, life-threatening condition is massive hemorrhage. Massive hemorrhage can kill people faster than an airway complication, because we don’t have much blood in our bodies in the first place (~5 liters is the average). Depending on the location of the wound, direct pressure, pressure dressing, wound packing (with or without a hemostatic agent) or tourniquets are the immediate field solutions to the problem. “The breakthrough paper that resulted was published in a 1996 issue of Military Medicine and ushered in the dawn of Tactical Combat Casualty Care (TCCC). TCCC launched a total reassessment of best practices in casualty management on the battlefield because of the penetrating wounding patterns found there. With 60 percent of preventable combat deaths identified as extremity hemorrhage, 33 percent as tension pneumothorax—a life-threatening chest injury— and 6 percent as airway obstruction, TCCC shifted the treatment priority from the standard prehospital protocol of airway management first to controlling the massive hemorrhage due to extremity trauma. This change meant that something as simple as applying a tourniquet could potentially save many lives on the battlefield. Military research began to focus on identifying a standard-issue tourniquet that was safe, effective, easy-to-apply and ruggedized for austere environments.” - North American Rescue - Winter 2012-2013 by Ricardo Flores Following the discussion with my friend I happened to have another similar discussion with a Navy Pararescue specialist. He reiterated the points covered in my previous discussion and emphasized that at the shooting range and in the back country it is imperative that you carry a tourniquet; and the only one that he recommended was the Combat Application Tourniquet (C-A-T) by North American Rescue - which is now the standard in the US military based on years of studies. “In 2004, the U.S. Army Institute of Surgical Research (USAISR) conducted a study of seven commercially available, off-the-shelf tourniquets for their effectiveness in stopping blood flow with the least amount of pain during application. Three of the seven were 100 percent clinically effective in occluding blood flow. However, USAISR recommended the C-A-T as the primary battlefield tourniquet based on its overall performance—less painful, easier to use, as well as smaller and lighter than the other tourniquets evaluated. In 2008, a study of battlefield data from a combat support hospital in Baghdad published in the Journal of Trauma validated the earlier USAIR conclusions. The C-A-T was identified as “the best combat tourniquet” In 2011, another study published in Military Medicine further validated the earlier studies and continued to hail the U.S. military’s primary tourniquet, the C-A-T, as the safest and most effective combat tourniquet requiring 30 percent less pressure to achieve success.” - North American Rescue - Winter 2012-2013 by Ricardo Flores Because of this discussion we updated our gear by purchasing a C-A-T tourniquet to replace our older gear. The CAT currently on the market is the 7th generation of the tourniquet and is recognized as the fastest, safest, and most effective prehospital field tourniquet available. It has proven to be 100% effective in occluding blood flow in both upper & lower extremities by the U.S. Army’s Institute of Surgical Research. The C-A-T comes in both black and orange. We purchased the orange version so that we can very easily locate it in our kit in an emergency situation. As with all tourniquets the main thing to remember if you have to apply one to a victim is to place it “high and tight” – high above the wound to stop the circulation above the point of bleeding and tight enough that you cannot put your fingers under the band; even if this is painful to the victim. Once in place do not ever remove the tourniquet unless you absolutely have to so that you can make it tighter because the bleeding restarts and you don’t have a second tourniquet to place adjacent to the initial tourniquet. With respect the C-A-T, “The Gen 7 CAT utilizes a durable windlass system with a patented free-moving internal band providing true circumferential pressure to the extremity. Once adequately tightened, bleeding will cease and the windlass is locked into place. A hook and loop windlass retention strap is then applied, securing the windlass to maintain pressure during casualty evacuation”. Here are the high level instructions for using the C-A-T tourniquet. It should be noted that tourniquets should normally only used for extremities (arms and legs) when the bleeding cannot be stopped by the use of direct pressure alone, if direct pressure cannot be effectively applied for any reason, or if it is clear that the injury is so massive that attempting to use direct pressure will fail and only waste valuable time. There is an intermediate option of “wound packing” that can be used if applying direct pressure is not sufficient to stop the bleeding and the wound is on the neck, armpit, shoulder or groin. Because of the critical internal organs - the only viable field solution to wounds to the chest, abdomen, lower back, pelvis and skull is applying direct pressure.
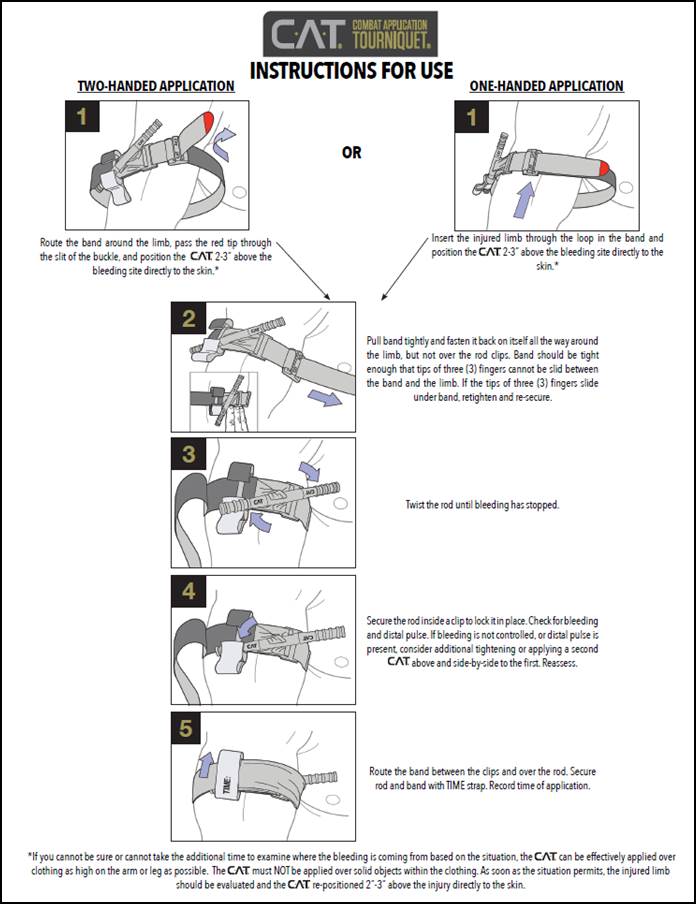
The nominal order of the steps that you should take to “stop the bleed” is:
If you want more details about the C-A-T Combat Application Tourniquet you can find it here: https://www.narescue.com/combat-application-tourniquet-c-a-t.html Here’s a great presentation by North American Rescue on “Small Limb Hemorrhage Control” that covers all this material in detail: https://www.narescue.com/education/cat-tourniquet-education/small-limb-hemorrhage-training-ppt.html In addition, other CAT Tourniquet Educational Materials can be found here: https://www.narescue.com/education/cat-tourniquet-education.html Just remember – with respect to traumatic bleeding – If it won’t quit - - - Tourniquet!
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
What's On This Page?Here's where we post reviews, questions, answers, thoughts and other information that's of general interest to our followers in a blog format. Categories
All
Archives
August 2023
|
|
|
Copyright 2016-2024 Hiking, Camping and Shooting |





 RSS Feed
RSS Feed